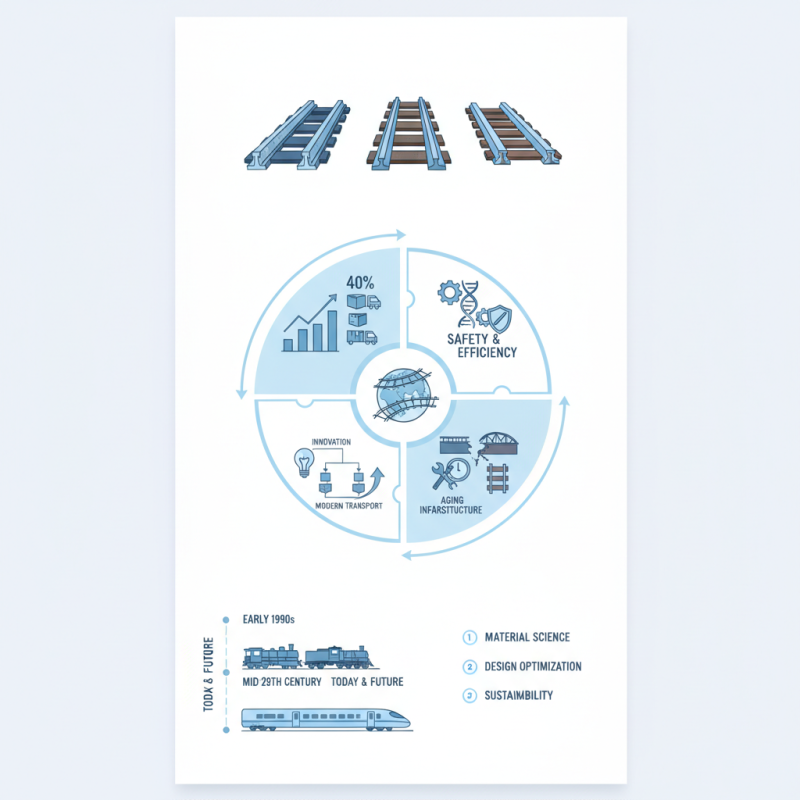
In today’s fast-paced world, the demand for efficient transportation systems continues to grow. According to the Association of American Railroads, over 40% of freight in the U.S. uses railroads, which underscores the importance of selecting the right Railroad Rail types. Dr. Emily Thornton, a railroad industry expert, states, "Choosing the right rail enhances safety and efficiency in transportation."
The evolution of Railroad Rail types has significantly impacted how goods are moved across regions. Modern rail systems incorporate advanced materials and designs to handle increasing loads. However, the focus on efficiency requires ongoing reflection and innovation. For instance, while heavy-duty rails provide durability, they might not always be suitable for lighter loads or urban transit systems.
Despite advancements, challenges remain in the industry. Aging infrastructure and maintenance demands can hinder progress. The need for better rail types reflects the imperative to adapt to changing transportation needs. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for shaping effective solutions in the Railroad Rail sector.
Rail transportation plays a crucial role in modern logistics and public transport. Different rail types cater to diverse needs. For freight services, heavy-duty rails are essential. These rails can support massive loads, ensuring efficient movement of goods. They often feature a larger profile to withstand the stress of heavy freight trains.
In addition, passenger services require a different approach. Lighter rails are designed for speed and comfort. They enable smoother rides and sharper turns, suitable for urban transit systems. The intersection of design and functionality is key. However, these lighter rails may wear out faster under heavy use. This raises questions about maintenance and sustainability.
Clearly, the choice of rail impacts efficiency and safety. As cities grow and freight demands increase, the rail industry must adapt. Innovations are needed to enhance durability without sacrificing performance. Balancing these factors is a continuous challenge for rail operators.
This chart displays the weight per meter of different railroad rail types used in modern freight and passenger services. Steel rails are the heaviest, providing durability, while composite and aluminum rails offer lightweight alternatives suitable for specific applications.
When selecting railroad rails for modern transportation needs, structural strength and durability are key considerations. Different rail types offer various advantages depending on the intended use. Steel rails, for instance, are commonly preferred for their strength, but they need proper maintenance. Regular inspections are essential to ensure their longevity.
Tips for maintaining rail strength: Frequent checks can prevent unexpected failures. Look for signs of wear or corrosion. This vigilance can save time and resources in the long run. Using appropriate technologies for inspection can also enhance reliability.
Certain rail types are heavier and broader, providing better stability under heavy loads. However, these may require advanced support systems. Engineers must balance weight with efficiency. A well-designed rail can improve safety and reduce costs, but the challenges remain. Continuous learning and adaptation are vital in this evolving field.
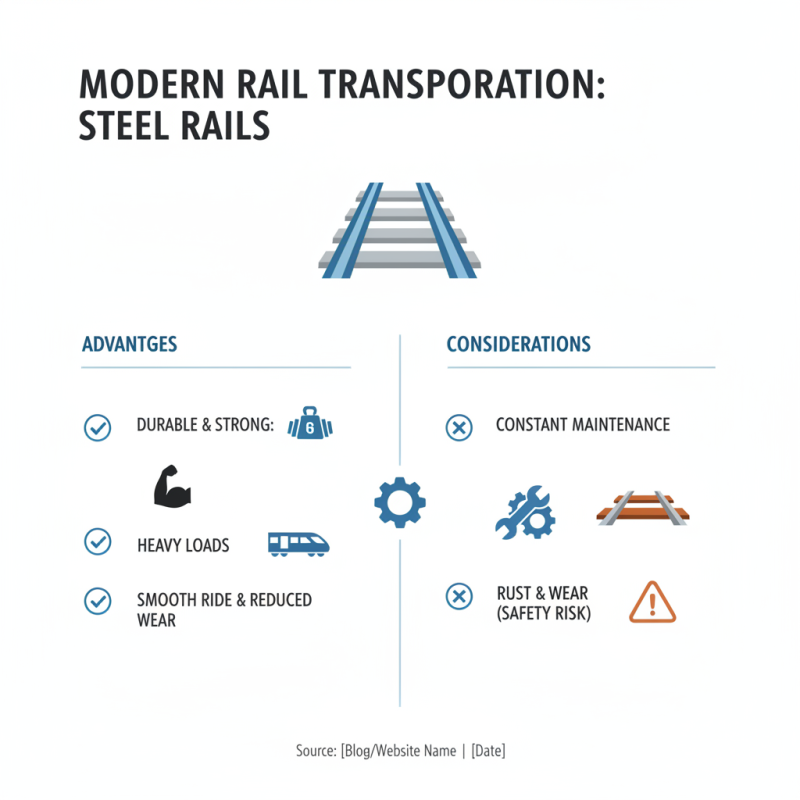
When it comes to modern transportation, the choice of rail type plays a crucial role. Steel rails are widely used. They are durable, strong, and able to withstand heavy loads. Steel provides a smooth ride, reducing wear on trains. However, they require constant maintenance due to wear and tear over time. Rust can also be an issue in certain environments, leading to safety concerns.
On the other hand, concrete rails have gained popularity. They are resistant to environmental factors, decreasing maintenance needs. A concrete rail also promotes stability for trains, allowing for better speed and efficiency. The downside? The initial cost can be high. Also, their installation requires careful planning and skilled labor. Balancing these factors is critical for any transportation project. Each material has its trade-offs, and choices are not always clear-cut.
Rail manufacturing has evolved significantly due to technological advancements. Modern rail types must cater to increasing demands for safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Reports indicate that investments in rail technology have grown by over 40% in the last decade. This surge is primarily driven by the need for improved materials and innovative designs.
New rail manufacturing techniques incorporate high-strength steel and composite materials. These materials provide better resistance to wear and fatigue. For example, research shows that advanced steel alloys can increase rail lifespan by 30%. This reduces the frequency of replacements and enhances safety.
Additionally, the integration of smart technologies is reshaping rail systems. Sensors embedded in rails can monitor structural integrity in real-time. Data analytics can forecast maintenance needs. However, not all rail systems can adapt to these changes easily. Some still lag in implementing such technologies, highlighting the need for ongoing development. The industry must reflect on its pace of innovation and prioritize modernization to meet future demands.

Modern rail systems play a crucial role in sustainable transportation. They reduce traffic congestion and lower emissions. Trains are more energy-efficient than cars or planes. However, rail transportation is not without its challenges. The construction and maintenance of rail infrastructure often disrupt local ecosystems. This impact on wildlife must be addressed.
The materials used in rails also matter. Steel is commonly used but has a significant carbon footprint. Exploring alternatives, such as recycled materials, could lessen this impact. Additionally, the use of electrified systems can decrease air pollution. Still, many regions rely on fossil fuels, which undermines sustainability goals.
Community involvement is essential for progress. Educating the public about the benefits of using rail can lead to increased ridership. Yet, ensuring that rail systems meet modern needs requires ongoing evaluation. There’s an urgent need for inclusive planning. Both environmental concerns and community voices should guide future developments in rail transport.